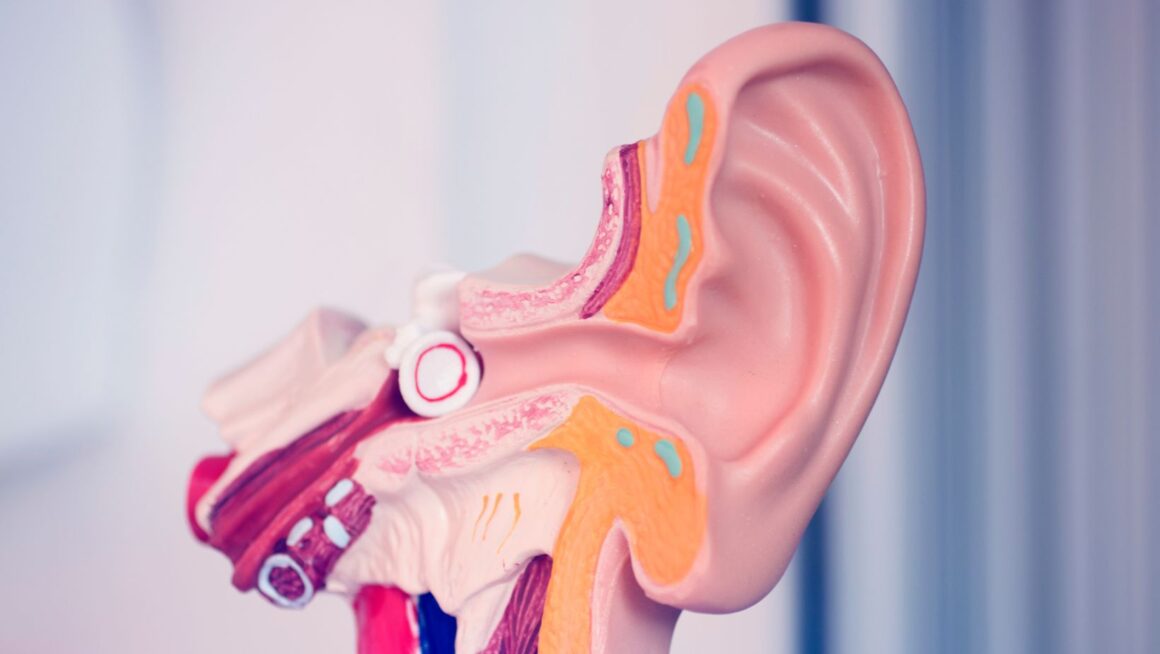
Maintaining good ear health is crucial for our overall well-being and quality of life. One of the common yet often misunderstood aspects of ear health is managing earwax accumulation. While it’s a natural and important part of ear health, excessive earwax can lead to discomfort and hearing problems. This guide will provide you with detailed insights into earwax management and ensure you’re equipped with practical knowledge to keep your ears healthy.
Understanding Earwax and Its Functions
Earwax, or cerumen, is a substance produced by glands in the ear canal. Its primary function is to protect the ears by trapping dust, microorganisms, and other particles that might enter the ear. Earwax also has lubricating properties, which help to prevent the ear canal from becoming too dry.
The Types of Earwax
- Dry Earwax: Typically found in East Asians and Native Americans, this type of earwax is flaky and gray.
- Wet Earwax: More common in other ethnic groups, this earwax is sticky and yellow to brown in color.
Both types of earwax perform the same basic functions but are influenced by genetic differences.
Safe Practices for Earwax Removal
Though earwax is beneficial, excessive accumulation can block the ear canal and impair hearing. It’s essential to handle earwax removal properly to avoid damaging the delicate structures inside the ear.
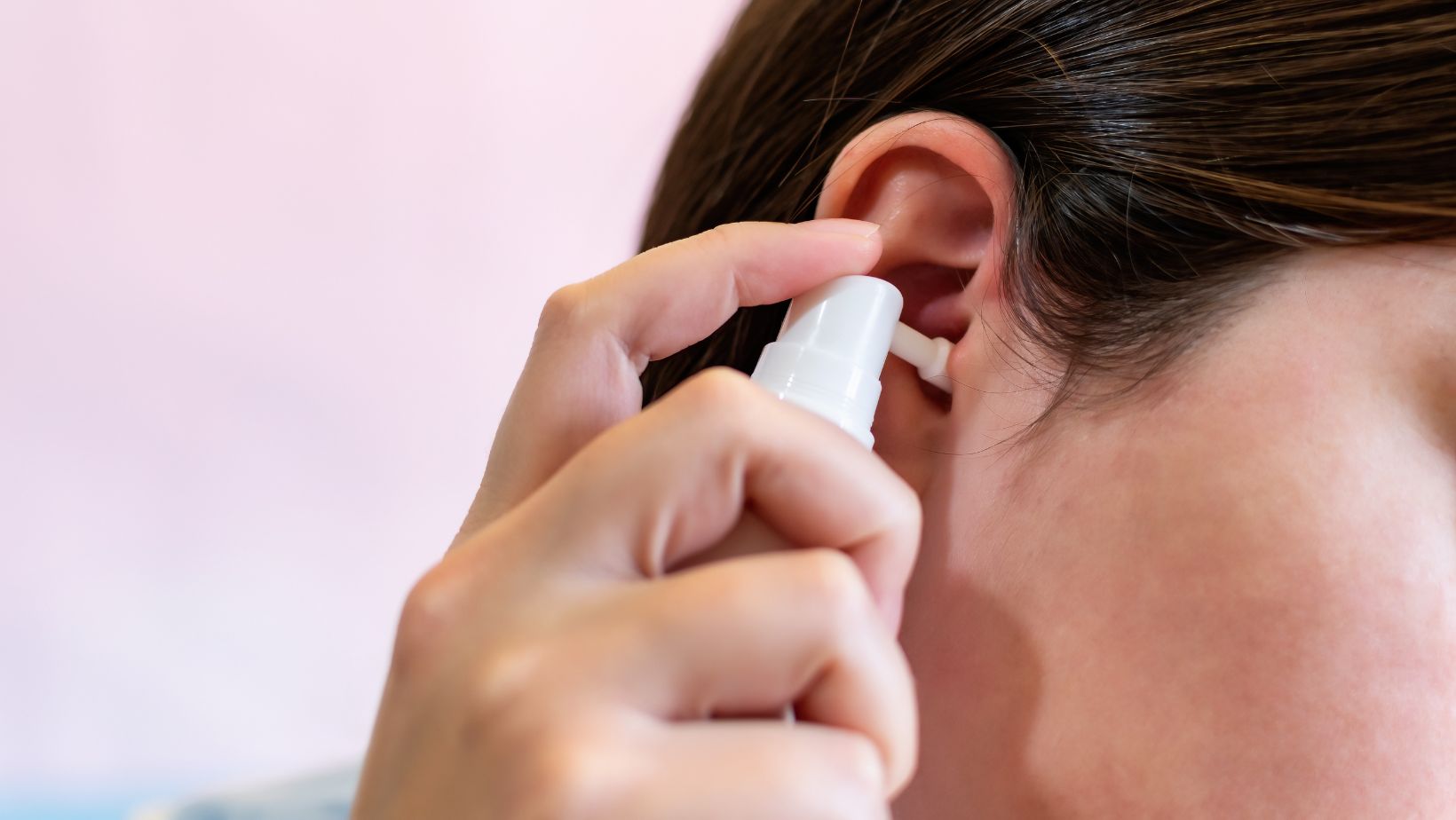
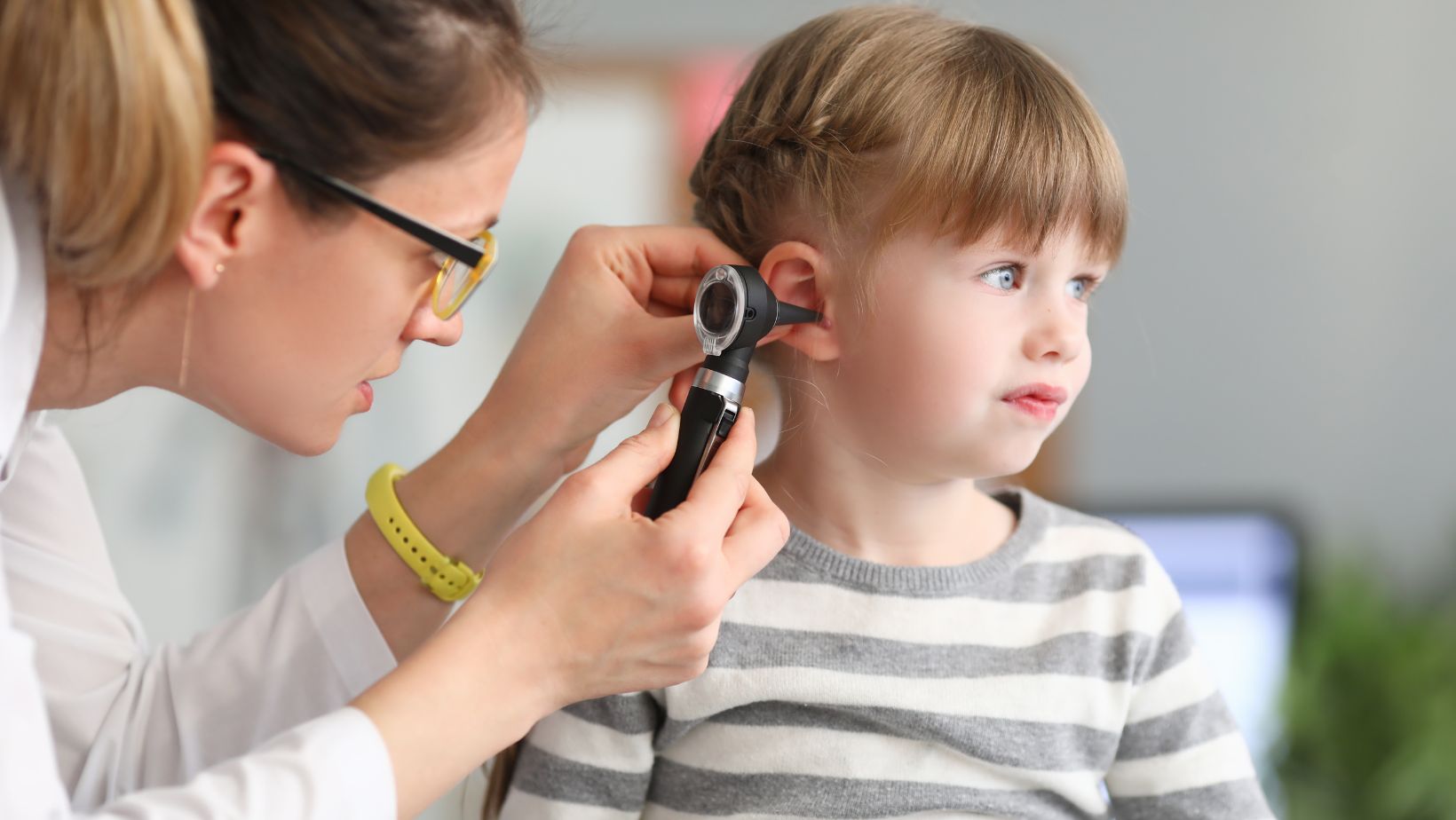
The safest approach to ear wax removal is often to let a professional such as an audiologist or a medical doctor handle it, especially if you suspect that the wax is heavily impacted.
Do’s and Don’ts of Earwax Removal
- Do: Use over-the-counter ear drops designed to soften earwax.
- Don’t: Insert cotton swabs or any objects into your ear canal, as this can push wax further into the ear and cause blockages or damage.
Home Remedies for Managing Earwax
For those who prefer to manage earwax at home, there are several safe methods you can employ:
Over-the-Counter Drops
These drops help soften the wax, making it easier to exit the ear naturally. Look for drops that contain hydrogen peroxide or glycerin.
Ear Irrigation Kits
These kits can be used at home to gently flush out the ear. It’s important to follow the instructions carefully to avoid causing any injury.
Warm Oil Drops
A few drops of warm (not hot) mineral oil or baby oil can also help soften the earwax. After applying the oil, lie on your side for a few minutes to let it work, and then sit up and wipe away any excess.
When to See a Professional
While home remedies can be effective for mild earwax problems, there are times when professional help is necessary. If you experience any of the following, it’s time to consult a healthcare provider:
- Persistent symptoms after trying home remedies
- Ear pain, itching, or discharge that suggests an infection
- Sudden or partial hearing loss
- A feeling of fullness in the ear
Professional Earwax Removal Techniques
Healthcare providers may use several methods to remove earwax safely:
- Microsuction: This technique uses a gentle vacuum to suck out the earwax.
- Ear Irrigation: A controlled stream of water is used to flush the wax out.
- Manual Removal: Special tools are used to carefully scoop out the earwax.
Preventing Excessive Earwax Buildup
Preventing problems before they start is an essential part of maintaining ear health. Here are some tips to prevent excessive earwax buildup:
- Avoid using cotton swabs or inserting any objects into your ears.
- Protect your ears from dust and other particles by wearing a cap or hat in windy, dusty conditions.
- Manage stress, as high-stress levels can increase the production of earwax.
The Connection Between Diet and Earwax Production
Believe it or not, your diet can impact earwax production. A diet high in omega-3 fatty acids and other nutrients can help maintain normal secretion and consistency of earwax.
Foods to Consider
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish like salmon and in flaxseeds.
- Magnesium: Present in nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
- Water: Staying hydrated helps maintain the moisture balance in the ears.
Keeping Ears Healthy
Earwax, though not often talked about, plays a significant role in our ear health. By understanding how to manage earwax properly, you can prevent discomfort and hearing issues while ensuring your ears remain healthy. Remember, when it comes to ear care, sometimes less is more. Avoid over-cleaning, and don’t hesitate to seek professional care when needed. Your ears are delicate instruments—treat them well, and they will continue to work effectively for you for years to come.