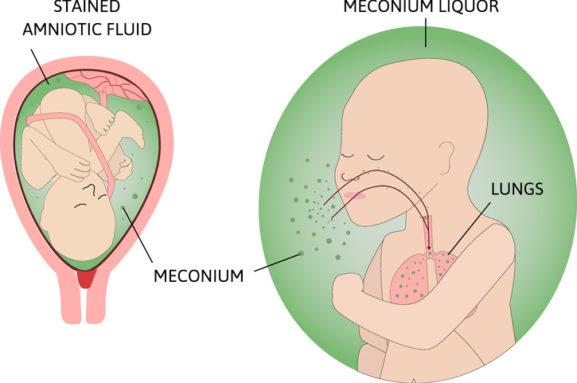
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome (MAS) occurs when a baby inhales meconium into their lungs, leading to respiratory issues. While MAS is relatively rare, it can significantly impact the baby’s health.
Finding the cause of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome is critical to managing the condition effectively. Early identification can improve the chances of recovery and help prevent severe complications. Therefore, in this blog, we will discuss everything about MAS, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and potential long-term effects.
What is Meconium Aspiration Syndrome?
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome occurs when a baby inhales a mixture of meconium (the first stool) and amniotic fluid into their lungs. Normally, the baby passes meconium after birth. Still, in some cases, the baby may release it into the amniotic fluid before delivery. If the baby inhales this mixture, it can block the airways, irritate the lungs, and lead to breathing problems.
Doctors commonly diagnose this condition in full-term or post-term babies, often linking it to complications during labor. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, MAS affects about 5-10% of full-term newborns, making it a relatively common issue.
Causes of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
Several factors can lead to MAS, including:
- Prolonged pregnancy: Post-term babies (over 40 weeks) are more likely to pass meconium into the amniotic fluid.
- Fetal distress: Stress caused by a lack of oxygen during labor may result in the release of meconium.
- Difficult labor: Prolonged or challenging deliveries can increase the risk of MAS.
- Maternal infections: Certain infections during pregnancy may trigger early passage of meconium.
- Umbilical cord complications: Issues like cord compression can reduce oxygen supply and lead to fetal stress.
Symptoms of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
The symptoms of meconium aspiration syndrome typically appear shortly after delivery, especially if meconium is visible in the amniotic fluid during labor.
Signs of MAS vary depending on its severity but may include:
- Rapid or labored breathing
- Bluish skin (cyanosis) due to low oxygen
- Nasal flaring or grunting sounds while breathing
- Low Apgar score (a measure of a newborn’s health)
- Coughing or choking after birth
- Swollen chest from trapped air
Diagnosis and Treatment of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
Doctors can diagnose MAS through physical examination and tests such as:
- Chest X-rays: To check for blockages or lung inflammation.
- Blood gas analysis: To assess oxygen and carbon dioxide levels.
- Pulse oximetry: To measure oxygen levels in the blood.
Most babies recover with proper care, but severe cases may require intensive medical support. Treatment depends on the severity of the condition and may include:
- Suctioning: Removing meconium from the baby’s airways immediately after delivery.
- Oxygen therapy: Providing extra oxygen to support breathing.
- Mechanical ventilation: In severe cases, a ventilator may be necessary to assist with breathing.
- Antibiotics: To prevent or treat infections.
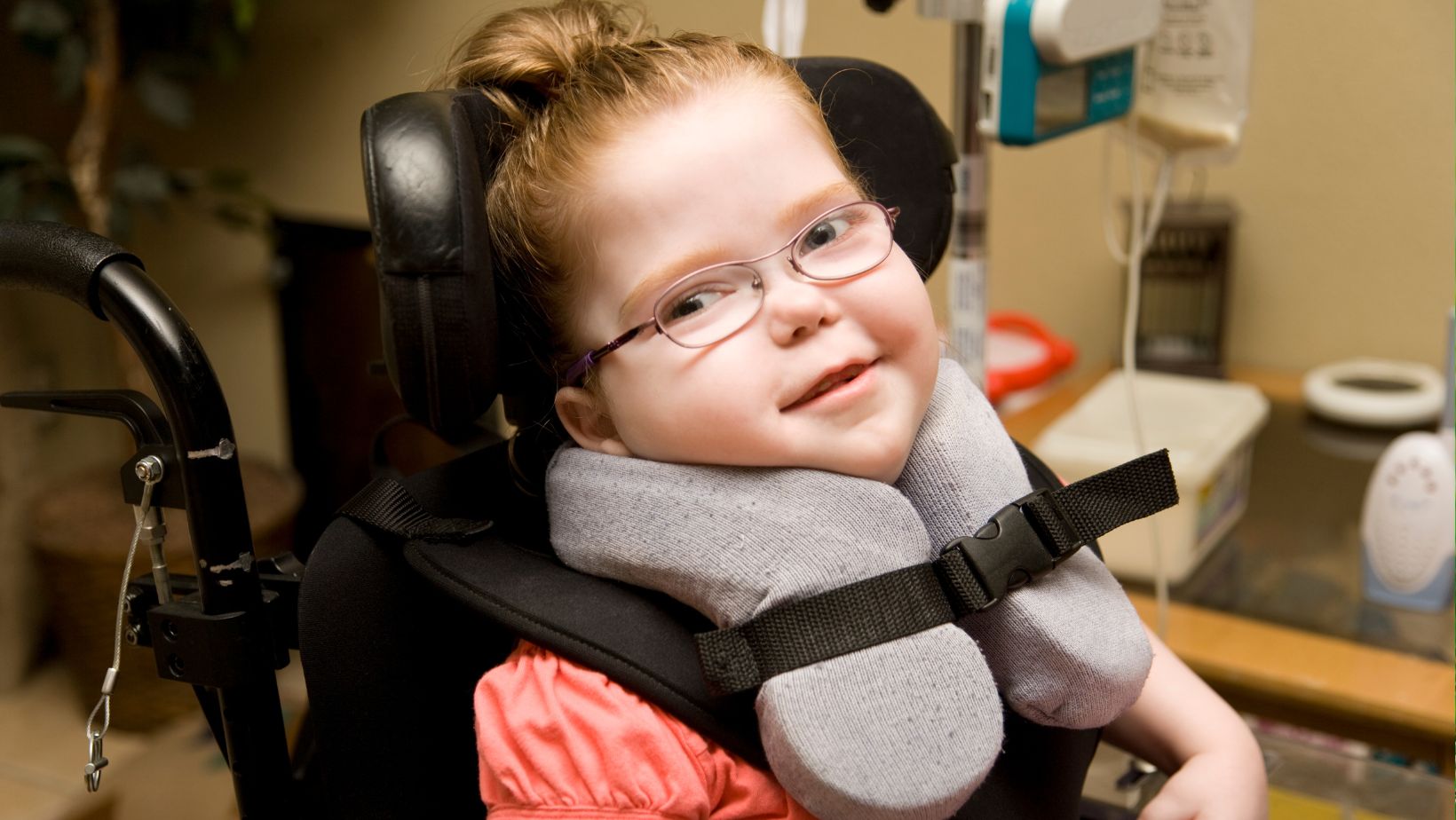
Long-Term Effects of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
While many babies fully recover from MAS, some may face long-term complications, such as:
- Chronic respiratory issues: Conditions like asthma or persistent wheezing.

- Developmental delays: Severe cases can lead to delayed growth or learning difficulties.
- Neurological problems: Lack of oxygen at birth may occasionally cause brain damage.
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers can help monitor and manage these potential effects.
Conclusion
While MAS can occur naturally, medical professionals must closely monitor high-risk pregnancies to minimize the chances of MAS and respond quickly if it arises. Early intervention is key to reducing the severity of the condition and ensuring better outcomes for the baby.
Unfortunately, in some cases, medical negligence, such as failure to monitor fetal distress, inadequate delivery room preparation, or delayed intervention, can increase the risk of MAS and worsen its effects. Parents whose children experience MAS due to medical negligence have the right to legal action. Stay aware and do not hesitate to take action if you are a victim.