Ear sensitivity and pain can be debilitating, affecting daily activities and overall quality of life. These issues can arise from various causes, including infections, exposure to loud noises, and underlying health conditions. Understanding the sources of ear sensitivity and pain, along with effective management strategies, is essential for achieving relief and maintaining ear health. This guide provides an informative and friendly overview of managing ear sensitivity and pain, helping you find quiet relief.
Understanding Ear Sensitivity and Pain
Ear sensitivity and pain, also known as earache or otalgia, can stem from different parts of the ear: the outer ear, middle ear, or inner ear. The nature of the pain can vary from a sharp, stabbing sensation to a dull, throbbing ache. Identifying the root cause is crucial for effective treatment.
Common Causes of Ear Sensitivity and Pain
One significant cause of ear pain is prolonged exposure to loud noises, which can lead to increased sensitivity and damage to the auditory system. For individuals who rely on devices such as hearing aids, ensuring they are correctly fitted and adjusted is crucial for comfort and effectiveness. If you’re in Melbourne, seeking professional advice on hearing aids Melbourne can help address sensitivity and improve hearing health.
Ear Infections
Ear infections are a prevalent cause of ear pain, particularly in children. Infections can occur in different parts of the ear:
- Outer Ear (Otitis Externa): Commonly known as swimmer’s ear, this infection occurs when bacteria or fungi infect the ear canal, often due to moisture.
- Middle Ear (Otitis Media): This infection typically follows a respiratory illness and causes fluid buildup behind the eardrum, leading to pain and pressure.
- Inner Ear (Labyrinthitis): Although less common, inner ear infections can cause severe pain and affect balance.
Earwax Buildup
Excessive earwax can cause blockages, leading to pain and discomfort. While earwax protects the ear canal by trapping dust and debris, too much of it can press against the eardrum or clog the ear canal, resulting in pain.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
The eustachian tubes connect the middle ear to the back of the throat and help equalize pressure. When these tubes become blocked, it can cause a feeling of fullness, pressure, and pain in the ears. Allergies, colds, and sinus infections are common culprits.
TMJ Disorders
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders can cause referred pain in the ear. The TMJ is located near the ear, and issues with the jaw joint or muscles can lead to pain in the ear area.
Noise-Induced Hearing Damage
Exposure to loud noises, whether sudden or chronic, can damage the delicate structures in the inner ear, leading to pain, sensitivity, and hearing loss. This condition is known as noise-induced hearing damage or noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL).
Strategies for Managing Ear Sensitivity and Pain
Effective management of ear sensitivity and pain involves addressing the underlying cause and adopting preventive measures to protect ear health. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Avoid Exposure to Loud Noises
Protecting your ears from loud noises is crucial for preventing noise-induced damage and reducing sensitivity.
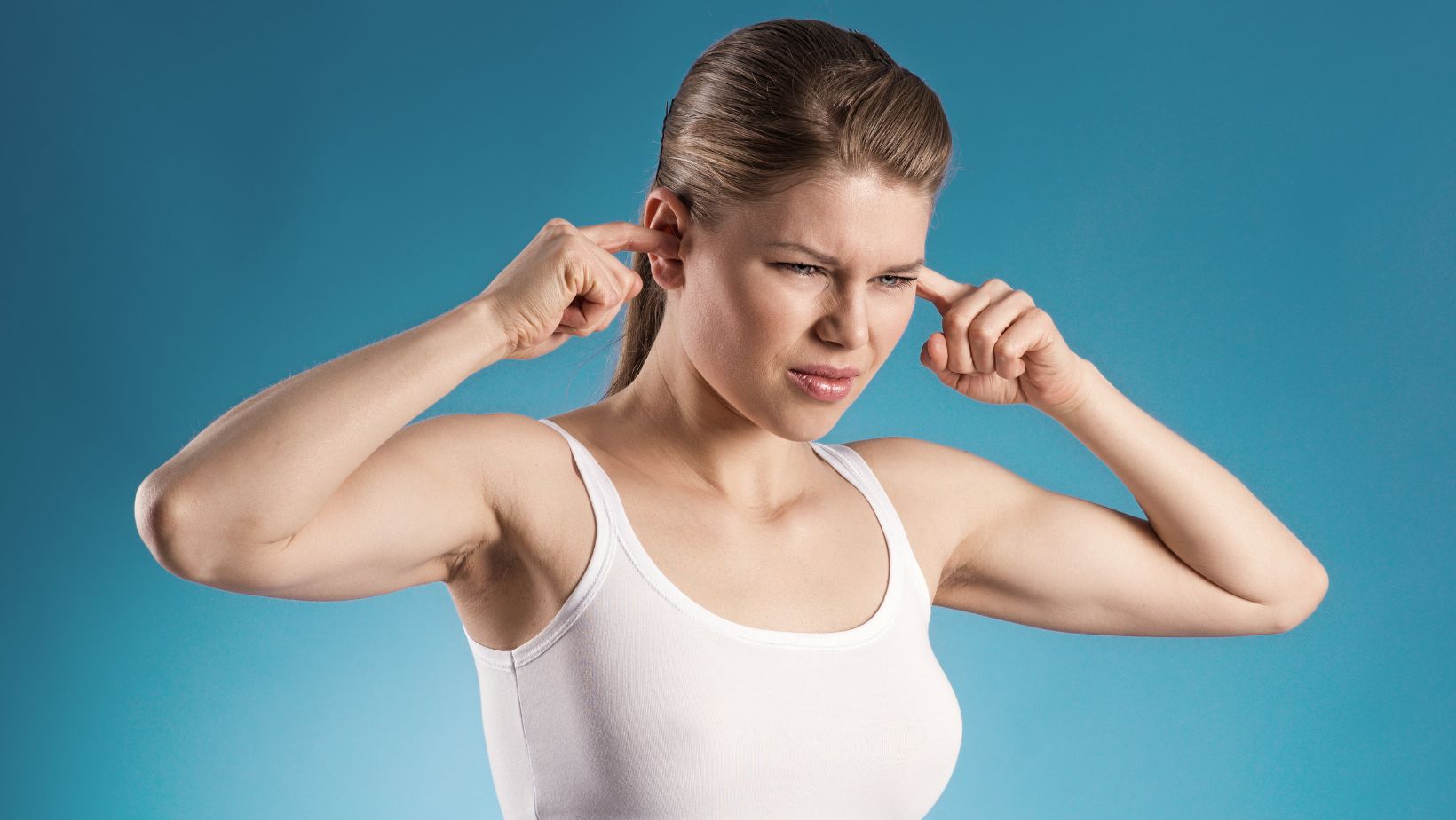

Use earplugs or noise-canceling headphones in noisy environments, such as concerts, construction sites, or when using power tools. Limiting exposure to loud sounds can help maintain ear health and prevent pain.
2. Practice Good Ear Hygiene
Maintaining good ear hygiene can prevent infections and blockages caused by earwax buildup. Avoid inserting objects into your ears, as this can push wax deeper and cause damage. Instead, clean the outer ear with a soft cloth and consider using ear drops to soften earwax if necessary. Regularly check your ears for signs of infection or irritation.
3. Seek Medical Attention for Infections
If you suspect an ear infection, seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare provider can diagnose the infection and prescribe appropriate treatment, such as antibiotics or antifungal medications. Early intervention can prevent complications and alleviate pain.
4. Manage Allergies and Sinus Issues
Allergies and sinus problems can lead to eustachian tube dysfunction and ear pain. Managing these conditions with antihistamines, decongestants, or nasal sprays can help keep the eustachian tubes clear and reduce ear pressure and pain. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice on managing allergies and sinus issues.
5. Use Warm Compresses
Applying a warm compress to the affected ear can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Use a warm cloth or heating pad and place it against the ear for 15-20 minutes. This can be especially soothing for ear infections and TMJ-related pain.
6. Address TMJ Disorders
If TMJ disorders are causing ear pain, seek treatment from a healthcare provider or dentist. Treatments may include physical therapy, oral splints or mouthguards, pain relievers, and lifestyle changes such as avoiding hard or chewy foods. Managing TMJ disorders can help alleviate referred pain in the ears.
7. Consider Hearing Protection
For individuals with increased sensitivity to sound, using hearing protection devices can help reduce discomfort. Custom earplugs or over-the-counter options designed for musicians, industrial workers, and individuals with sensitive hearing can provide relief in noisy environments.
8. Get Professional Advice on Hearing Aids
If you use hearing aids, ensure they are properly fitted and adjusted to avoid discomfort and sensitivity. Hearing aids should be comfortable and enhance your hearing without causing pain. Seek advice from professionals to find the best solution for your needs.
9. Stay Hydrated
Staying hydrated can help maintain the health of your ear canals and prevent dryness that can lead to irritation and pain. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your body and ears hydrated.
10. Avoid Q-tips and Other Objects
Inserting objects like Q-tips into your ear canal can cause damage and push earwax deeper into the ear. Avoid using these objects and instead, gently clean the outer ear with a soft cloth.
When to See a Doctor
While many cases of ear sensitivity and pain can be managed with home remedies and preventive measures, it is essential to seek medical attention if you experience:
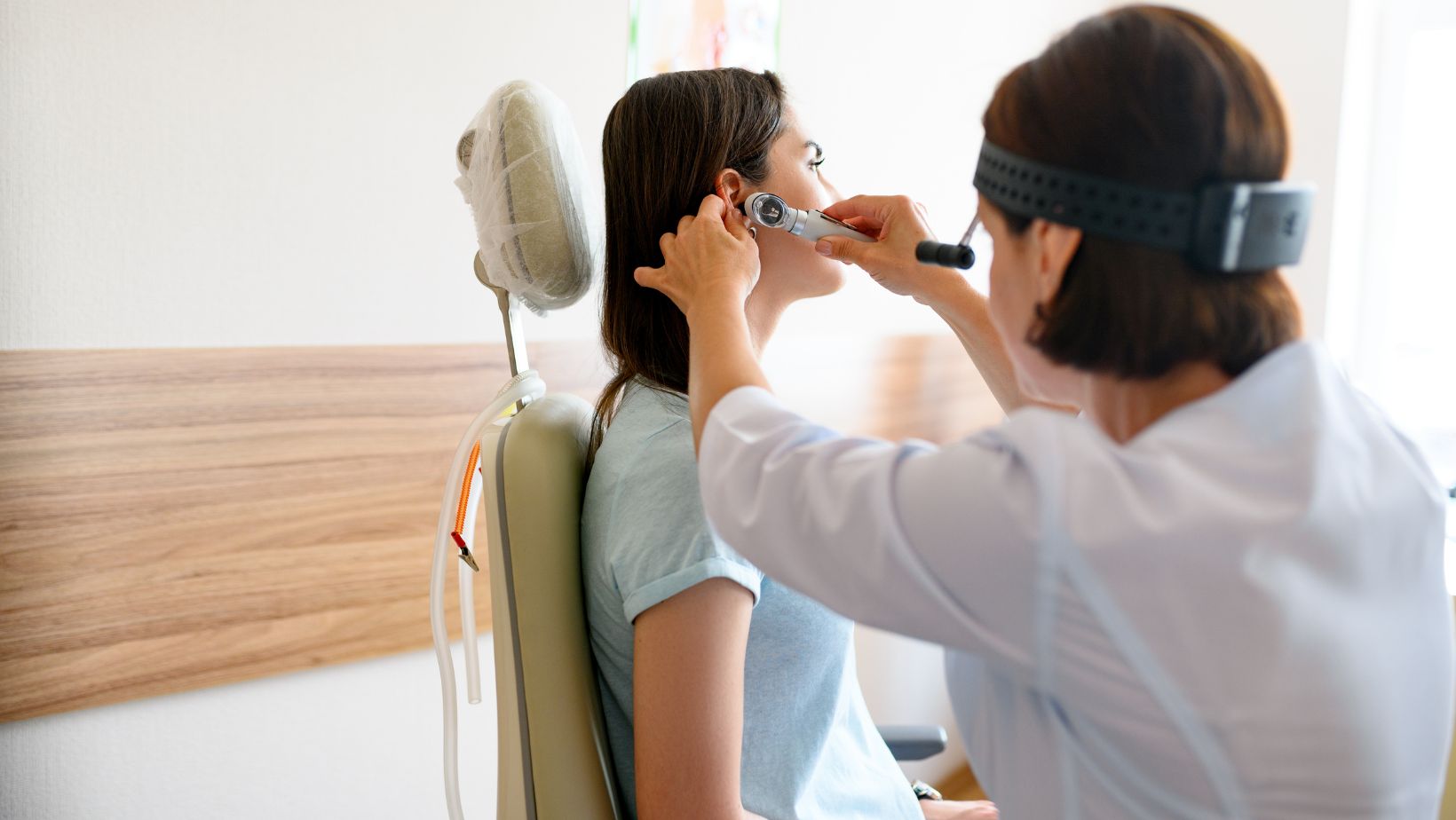
- Severe or persistent ear pain
- Hearing loss or changes in hearing
- Fluid drainage from the ear
- Dizziness, vertigo, or balance problems
- Symptoms that do not improve with home treatment
A healthcare professional can provide a thorough evaluation, diagnose the underlying cause, and recommend appropriate treatments to address your ear issues effectively.
Final Thoughts
Managing ear sensitivity and pain involves a combination of preventive measures, proper ear hygiene, and seeking professional advice when necessary. Understanding the common causes of ear discomfort, such as infections, earwax buildup, and noise-induced damage, can help you take proactive steps to protect your ears and maintain their health. Whether it’s using hearing protection, practicing good hygiene, or consulting with experts, there are many ways to find relief and keep your ears healthy. By staying informed and proactive, you can enjoy quiet relief and maintain your overall well-being.