Introduction
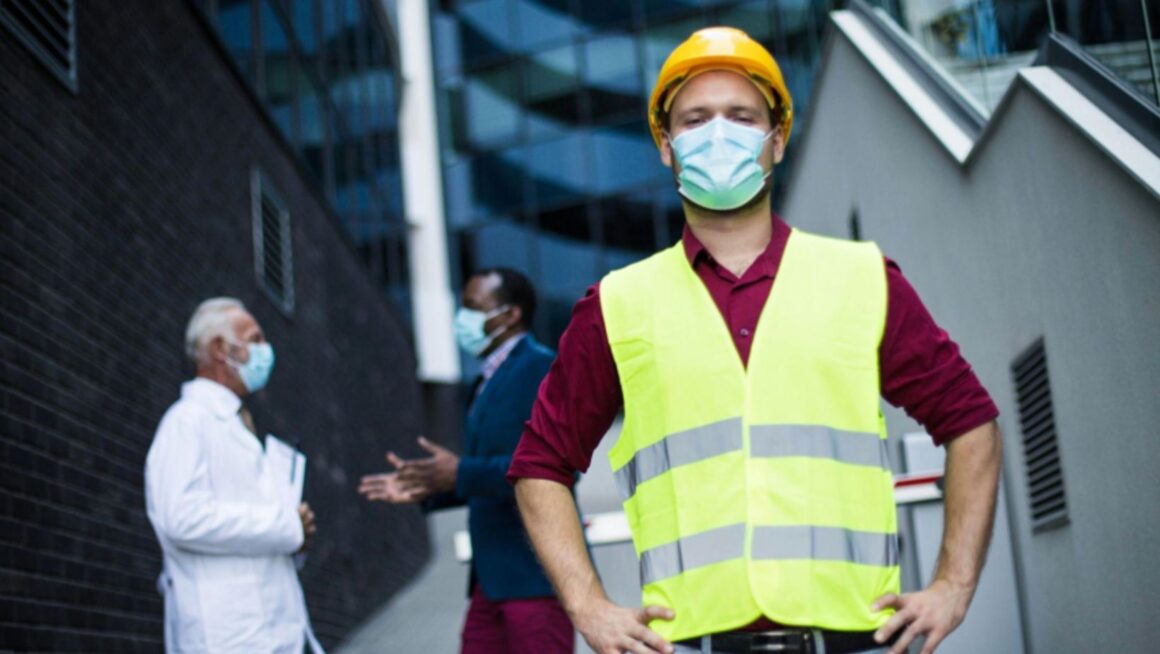
Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) training is a cornerstone of creating and maintaining a safe workplace. This training equips employees and employers with the necessary knowledge and skills to identify, assess, and mitigate potential hazards. By fostering a culture of safety, OHS training not only prevents accidents and reduces injuries but also ensures compliance with legal standards. This proactive approach enhances overall productivity, morale, and well-being in the workplace.
Understanding Workplace Hazards
OHS training plays a crucial role in helping employees and employers identify and understand common workplace hazards. By recognizing these dangers, workplaces can implement effective strategies to prevent accidents and injuries. Here’s a closer look at the types of hazards covered in OHS training:
Physical Hazards
These hazards are often the most visible and immediate threats in the workplace. They include slips, trips, falls, noise, and vibrations. These programs teach participants to spot unsafe conditions and, through manual handling training, the ability to work around the problem in a safe manner. Also, strategies are developed for preventive measures, such as maintaining clean and clutter-free work areas, using proper safety signage, and ensuring regular maintenance of equipment.
Chemical Hazards
Exposure to hazardous chemicals can lead to severe health issues. OHS training helps attendees understand Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to minimize exposure. Workers learn how to identify chemical hazards and take the necessary precautions to protect themselves and their colleagues.
Biological Hazards
Biological hazards involve exposure to harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. OHS training helps employees recognize potential sources of biological hazards, implement proper hygiene practices, and use protective measures to prevent infection and contamination. This is especially important in industries like healthcare, where the risk of biological exposure is higher.
Risk Assessment and Management
OHS training emphasizes a systematic risk assessment process to identify and evaluate workplace hazards. This process involves three key steps:
- Hazard Identification: Identify potential hazards in the workplace, ranging from physical dangers like wet floors to chemical risks from substances.
- Risk Evaluation: Assess the likelihood and severity of incidents related to each hazard. This helps prioritize which risks need immediate action.
- Control Measures: Implement strategies to eliminate or reduce risks. These can include engineering controls (e.g., safety guards), administrative controls (e.g., training and policies), and personal protective equipment (PPE).
Evaluating Risks
Evaluate risks by considering the frequency of exposure, the number of people affected, and the potential impact of incidents. Implement control measures effectively by:
● Eliminating Hazards: Remove hazards entirely whenever possible.
● Engineering Controls: Modify the workplace to reduce risks, such as installing ventilation systems.
● Administrative Controls: Establish policies and training programs to minimize exposure.
● PPE: Provide and mandate the use of appropriate personal protective equipment as a last line of defense.
Emergency Preparedness and Response
OHS training covers comprehensive emergency procedures and response plans to ensure quick and effective action during crises. Key components include:
● Fire Safety: Evacuation routes, use of fire extinguishers, and assembly points.
● Medical Emergencies: First aid procedures, contacting emergency services, and providing essential care until help arrives.
● Natural Disasters: Shelter-in-place strategies, communication plans, and post-disaster recovery steps.
Importance of Preparedness
Being prepared for various emergencies is crucial for minimizing harm and saving lives. Preparedness ensures:
● Quick Response: Immediate, appropriate actions can prevent escalation and mitigate damage.

● Safety Assurance: Employees feel secure knowing there are plans in place to handle emergencies.
● Compliance: Adhering to safety regulations and standards to avoid legal repercussions.
Role of Emergency Drills and Regular Practice
Emergency drills and regular practice are vital for:
● Building Familiarity: Ensuring all employees know their roles and actions during an emergency.
● Identifying Weaknesses: Revealing gaps in the response plan that need improvement.
● Enhancing Coordination: Promoting teamwork and efficient communication during real incidents.
Regular drills and ongoing training reinforce these plans, keeping preparedness at its peak and ensuring that employees can act swiftly and effectively in an emergency.
Ergonomics and Workplace Design
OHS training emphasizes the importance of ergonomics, focusing on designing workspaces that fit the needs of employees to enhance comfort and efficiency. Key principles include:
● Neutral Posture: Encouraging natural alignment of the spine, reducing strain on muscles and joints.
● Movement Variety: Promoting regular changes in posture and movement to avoid repetitive strain.
● Adjustability: Ensuring workstations can be tailored to individual needs, accommodating various body types and work habits.
Benefits of Ergonomic Practices
Implementing ergonomic practices can significantly prevent injuries and boost productivity by:
● Reducing Musculoskeletal Disorders: Proper ergonomic setups minimize the risk of developing conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome and back pain.
● Enhancing Comfort: A well-designed workspace reduces fatigue and discomfort, allowing employees to focus and perform better.

● Improving Efficiency: Ergonomic tools and practices streamline workflows, reducing unnecessary movements and enhancing overall efficiency.
Ergonomic Tips
Practical ergonomic adjustments and tools that can be implemented include:
● Adjustable Chairs: Chairs with lumbar support and adjustable heights help maintain a neutral posture.
● Sit-Stand Desks: Allowing employees to alternate between sitting and standing throughout the day to reduce strain.
● Keyboard and Mouse Placement: Positioning keyboards and mice at elbow height and within easy reach to prevent wrist strain.
● Monitor Height and Distance: Setting monitors at eye level and arm’s length away to reduce neck and eye strain.
● Footrests: Providing footrests for those whose feet do not comfortably reach the floor, ensuring proper leg support.
Conclusion
The value of ongoing OHS training cannot be overstated. It equips employees with the knowledge and skills needed to prevent accidents and injuries, fostering a culture of safety and compliance. By participating in OHS training programs, employees can significantly enhance their understanding of workplace safety, contributing to a healthier, more secure work environment.
We encourage everyone to engage in OHS training programs. Doing so will not only improve individual safety but also promote a collective commitment to maintaining a safe workplace for all.